Adsorption and Desorption of Chemical Warfare Agent Simulants on Silica Surfaces with Hydrophobic Coating
Vol. 34, No. 7, pp. 1967-1971, Jul. 2013
 10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.7.1967
10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.7.1967
Tumbnail
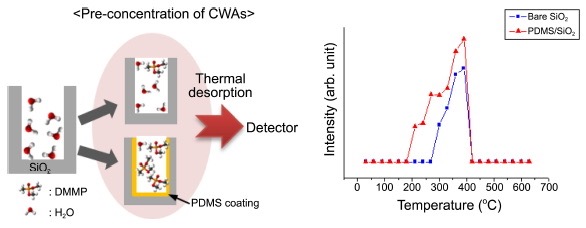
Abstract
Statistics
Cumulative Counts from November, 2022
Multiple requests among the same browser session are counted as one view. If you mouse over a chart, the values of data points will be shown.
Multiple requests among the same browser session are counted as one view. If you mouse over a chart, the values of data points will be shown.
|
|
Cite this article
[IEEE Style]
E. J. Park and Y. D. Kim, "Adsorption and Desorption of Chemical Warfare Agent Simulants on Silica Surfaces with Hydrophobic Coating," Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, vol. 34, no. 7, pp. 1967-1971, 2013. DOI: 10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.7.1967.
[ACM Style]
Eun Ji Park and Young Dok Kim. 2013. Adsorption and Desorption of Chemical Warfare Agent Simulants on Silica Surfaces with Hydrophobic Coating. Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, 34, 7, (2013), 1967-1971. DOI: 10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.7.1967.

