Effect of Valence Electron Concentration on Elastic Properties of 4d Transition Metal Carbides MC (M = Y, Zr, Nb, and Rh)
Vol. 34, No. 7, pp. 2171-2175, Jul. 2013
 10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.7.2171
10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.7.2171
Tumbnail
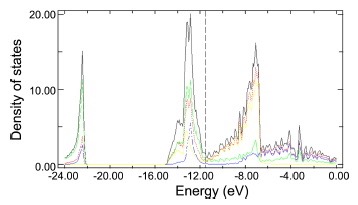
Abstract
Statistics
Cumulative Counts from November, 2022
Multiple requests among the same browser session are counted as one view. If you mouse over a chart, the values of data points will be shown.
Multiple requests among the same browser session are counted as one view. If you mouse over a chart, the values of data points will be shown.
|
|
Cite this article
[IEEE Style]
D. Kang, "Effect of Valence Electron Concentration on Elastic Properties of 4d Transition Metal Carbides MC (M = Y, Zr, Nb, and Rh)," Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, vol. 34, no. 7, pp. 2171-2175, 2013. DOI: 10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.7.2171.
[ACM Style]
Dae-Bok Kang. 2013. Effect of Valence Electron Concentration on Elastic Properties of 4d Transition Metal Carbides MC (M = Y, Zr, Nb, and Rh). Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, 34, 7, (2013), 2171-2175. DOI: 10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.7.2171.

