Kinetics and Mechanism of the Aminolyses of Bis(2-oxo-3-oxazolidinyl) Phosphinic Chloride in Acetonitrile
Vol. 34, No. 11, pp. 3218-3222, Nov. 2013
 10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.11.3218
10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.11.3218
-
Phosphoryl transfer reaction Anilinolysis Pyridinolysis Bis(2-oxo-3-oxazolidinyl) phosphinic chloride Deuterium kinetic isotope effect
Tumbnail
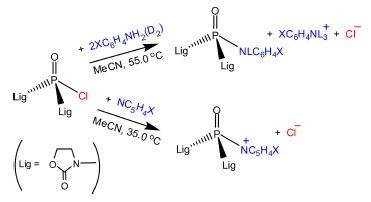
Abstract
Statistics
Cumulative Counts from November, 2022
Multiple requests among the same browser session are counted as one view. If you mouse over a chart, the values of data points will be shown.
Multiple requests among the same browser session are counted as one view. If you mouse over a chart, the values of data points will be shown.
|
|
Cite this article
[IEEE Style]
H. R. Barai and H. W. Lee, "Kinetics and Mechanism of the Aminolyses of Bis(2-oxo-3-oxazolidinyl) Phosphinic Chloride in Acetonitrile," Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, vol. 34, no. 11, pp. 3218-3222, 2013. DOI: 10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.11.3218.
[ACM Style]
Hasi Rani Barai and Hai Whang Lee. 2013. Kinetics and Mechanism of the Aminolyses of Bis(2-oxo-3-oxazolidinyl) Phosphinic Chloride in Acetonitrile. Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, 34, 11, (2013), 3218-3222. DOI: 10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.11.3218.

