Butein Disrupts Hsp90’s Molecular Chaperoning Function and Exhibits Anti-proliferative Effects Against Drug-resistant Cancer Cells
Vol. 34, No. 11, pp. 3345-3349, Nov. 2013
 10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.11.3345
10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.11.3345
Tumbnail
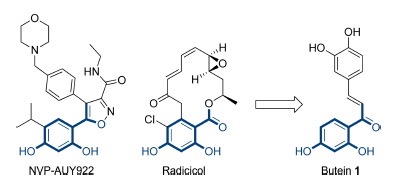
Abstract
Statistics
Cumulative Counts from November, 2022
Multiple requests among the same browser session are counted as one view. If you mouse over a chart, the values of data points will be shown.
Multiple requests among the same browser session are counted as one view. If you mouse over a chart, the values of data points will be shown.
|
|
Cite this article
[IEEE Style]
Y. H. Seo, "Butein Disrupts Hsp90’s Molecular Chaperoning Function and Exhibits Anti-proliferative Effects Against Drug-resistant Cancer Cells," Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, vol. 34, no. 11, pp. 3345-3349, 2013. DOI: 10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.11.3345.
[ACM Style]
Young Ho Seo. 2013. Butein Disrupts Hsp90’s Molecular Chaperoning Function and Exhibits Anti-proliferative Effects Against Drug-resistant Cancer Cells. Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, 34, 11, (2013), 3345-3349. DOI: 10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.11.3345.

