Kinetics and Mechanism of Pyridinolyses of Ethyl Methyl and Ethyl Propyl Chlorothiophosphates in Acetonitrile
Vol. 34, No. 11, pp. 3372-3376, Nov. 2013
 10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.11.3372
10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.11.3372
-
Thiophosphoryl transfer reaction Pyridinolysis Ethyl methyl and ethyl propyl chlorothiophosphates Biphasic concave upward free energy relationship Stepwise mechanism
Tumbnail
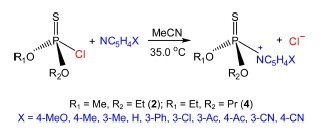
Abstract
Statistics
Cumulative Counts from November, 2022
Multiple requests among the same browser session are counted as one view. If you mouse over a chart, the values of data points will be shown.
Multiple requests among the same browser session are counted as one view. If you mouse over a chart, the values of data points will be shown.
|
|
Cite this article
[IEEE Style]
H. R. Barai and H. W. Lee, "Kinetics and Mechanism of Pyridinolyses of Ethyl Methyl and Ethyl Propyl Chlorothiophosphates in Acetonitrile," Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, vol. 34, no. 11, pp. 3372-3376, 2013. DOI: 10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.11.3372.
[ACM Style]
Hasi Rani Barai and Hai Whang Lee. 2013. Kinetics and Mechanism of Pyridinolyses of Ethyl Methyl and Ethyl Propyl Chlorothiophosphates in Acetonitrile. Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, 34, 11, (2013), 3372-3376. DOI: 10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.11.3372.

