Spectrometric Determination of Rhodamine B in Chili Powder After Molecularly Imprinted Solid Phase Extraction
Vol. 34, No. 11, pp. 3381-3386, Nov. 2013
 10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.11.3381
10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.11.3381
-
Rhodamine B Chili powder Molecularly imprinted polymers Solid-phase extraction Multiwalled carbon nanotubes
Tumbnail
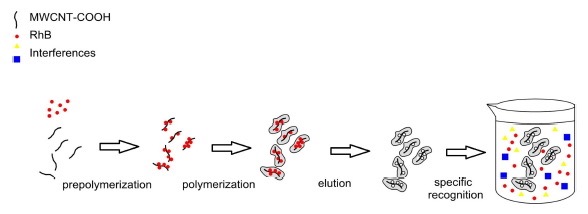
Abstract
Statistics
Cumulative Counts from November, 2022
Multiple requests among the same browser session are counted as one view. If you mouse over a chart, the values of data points will be shown.
Multiple requests among the same browser session are counted as one view. If you mouse over a chart, the values of data points will be shown.
|
|
Cite this article
[IEEE Style]
X. Liu, X. Zhang, Q. Zhou, B. Bai, S. Ji, "Spectrometric Determination of Rhodamine B in Chili Powder After Molecularly Imprinted Solid Phase Extraction," Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, vol. 34, no. 11, pp. 3381-3386, 2013. DOI: 10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.11.3381.
[ACM Style]
Xiuying Liu, Xuan Zhang, Qian Zhou, Bing Bai, and Shujuan Ji. 2013. Spectrometric Determination of Rhodamine B in Chili Powder After Molecularly Imprinted Solid Phase Extraction. Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, 34, 11, (2013), 3381-3386. DOI: 10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.11.3381.

