Absorption of SO2 at High Temperatures by Ionic Liquids and the Absorption Mechanism
Vol. 35, No. 9, pp. 2791-2796, Sep. 2014
 10.5012/bkcs.2014.35.9.2791
10.5012/bkcs.2014.35.9.2791
Tumbnail
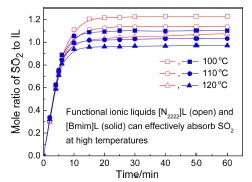
Abstract
Statistics
Cumulative Counts from November, 2022
Multiple requests among the same browser session are counted as one view. If you mouse over a chart, the values of data points will be shown.
Multiple requests among the same browser session are counted as one view. If you mouse over a chart, the values of data points will be shown.
|
|
Cite this article
[IEEE Style]
S. Tian, Y. Hou, W. Wu, S. Ren, J. Qian, "Absorption of SO2 at High Temperatures by Ionic Liquids and the Absorption Mechanism," Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, vol. 35, no. 9, pp. 2791-2796, 2014. DOI: 10.5012/bkcs.2014.35.9.2791.
[ACM Style]
Shidong Tian, Yucui Hou, Weize Wu, Shuhang Ren, and Jianguo Qian. 2014. Absorption of SO2 at High Temperatures by Ionic Liquids and the Absorption Mechanism. Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, 35, 9, (2014), 2791-2796. DOI: 10.5012/bkcs.2014.35.9.2791.

